Introduction
In the golden years of life, maintaining bone health becomes crucial for seniors. Osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened bones, poses a significant threat. This article explores the importance of bone health in seniors and strategies to prevent osteoporosis.
Understanding Osteoporosis
Definition and Causes
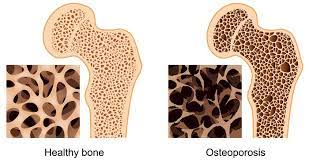
Osteoporosis is a bone disease that occurs when the body loses too much bone, makes too little bone, or both. Aging, hormonal changes, and nutritional deficiencies contribute to its development.
Risk Factors
Various factors, including age, gender, and family history, increase the risk of developing osteoporosis. Understanding these risk factors is vital for effective prevention.
Signs and Symptoms
Silent Nature of Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is often called a “silent disease” because it progresses without noticeable symptoms until a fracture occurs. Recognizing the silent nature of this condition is key to early intervention.
Identifying Warning Signs
Subtle signs such as height loss, stooped posture, and frequent fractures may indicate the presence of osteoporosis. Being aware of these warning signs is essential for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Impact on Seniors
Increased Fracture Risk
Seniors with osteoporosis face an increased risk of fractures, particularly in the hip, spine, and wrist. These fractures can significantly impact their overall well-being.
Reduced Quality of Life
Chronic pain, limited mobility, and fear of falling can lead to a reduced quality of life for seniors with osteoporosis. Addressing these aspects is crucial for holistic care.
Prevention Strategies
Importance of Nutrition
A well-balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D plays a pivotal role in maintaining bone health. Exploring dietary sources and supplements is essential for seniors.
Weight-Bearing Exercises
Regular exercise, especially weight-bearing activities, helps strengthen bones and improve balance. Tailoring exercise routines to the needs and capabilities of seniors is crucial.
Lifestyle Modifications
Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol consumption contribute to overall health and help prevent osteoporosis. Lifestyle changes are integral to long-term well-being.
Supplements for Bone Health
Vitamin D and Calcium
Supplements of vitamin D and calcium are often recommended for seniors to support bone health. Understanding proper dosage and potential interactions is vital.
Other Essential Nutrients
In addition to calcium and vitamin D, other nutrients like magnesium, phosphorus, and vitamin K contribute to bone health. A comprehensive approach ensures overall well-being.
Regular Health Checkups
Bone Density Testing
Regular bone density tests are essential for early detection and monitoring of osteoporosis. Seniors should discuss the frequency and necessity of these tests with their healthcare providers.
Monitoring Overall Health
Incorporating routine health checkups allows healthcare professionals to assess the overall well-being of seniors, addressing potential issues promptly.
Medication Options
Prescription Medications
In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe medications to slow down bone loss and prevent fractures. Understanding the benefits and potential side effects is crucial.
Side Effects and Considerations
Seniors should be aware of potential side effects of osteoporosis medications and discuss any concerns with their healthcare providers. Open communication is key for effective treatment.
Creating a Senior-Friendly Environment
Home Safety Measures
Implementing safety measures at home, such as removing tripping hazards and installing grab bars, helps create a senior-friendly environment.
Fall Prevention Strategies
Educating seniors about fall prevention strategies, including proper footwear and exercise, reduces the risk of fractures and injuries.
The Role of Healthcare Professionals
Geriatric Specialists
Consulting geriatric specialists who focus on senior health can provide personalized care and guidance in managing osteoporosis.
Collaboration with Primary Care Physicians
Effective collaboration between healthcare professionals, including primary care physicians, ensures a holistic approach to senior health.
Community Support and Resources
Support Groups
Engaging in support groups allows seniors to share experiences and strategies for coping with osteoporosis. Emotional support is as crucial as physical care.
Educational Programs
Participating in educational programs on bone health provides seniors with valuable information and tools to manage osteoporosis effectively.
Personal Stories
Real-Life Experiences
Sharing real-life experiences of seniors who have successfully managed osteoporosis inspires and educates others facing similar challenges.
Learning from Others
Learning from others’ journeys fosters a sense of community and empowers seniors to take charge of their bone health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can osteoporosis be reversed in seniors?
Osteoporosis is a progressive condition, but with proper intervention, further bone loss can be prevented. Reversal may not be entirely possible, but management strategies can improve bone health.
What foods are rich in calcium and vitamin D?
Dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods are excellent sources of calcium and vitamin D. A well-balanced diet incorporating these elements supports bone health.
Are there exercises suitable for seniors with limited mobility?
Yes, chair exercises, gentle stretching, and water aerobics are suitable for seniors with limited mobility. Consulting a healthcare professional for personalized exercise recommendations is advisable.
How often should seniors have bone density tests?
The frequency of bone density tests depends on individual risk factors and healthcare provider recommendations. Typically, seniors may undergo these tests every 1-2 years.
Can osteoporosis be prevented entirely?
While complete prevention may not be possible, adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, significantly reduces the risk of developing osteoporosis.
Conclusion
In the journey of aging, prioritizing bone health is essential for seniors. By understanding the nuances of osteoporosis and implementing preventive strategies, seniors can enjoy a higher quality of life. Regular checkups, a supportive environment, and community engagement contribute to holistic well-being.